¿Las farolas solares son suficientemente luminosas? ¿Qué nivel de lux necesito?
Light measurement for solar street lighting systems
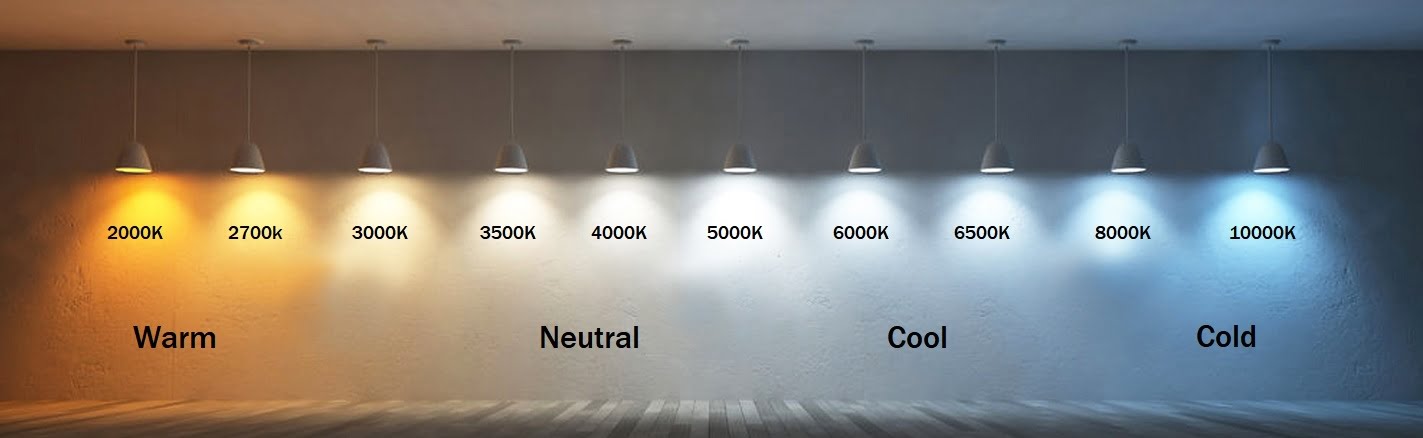
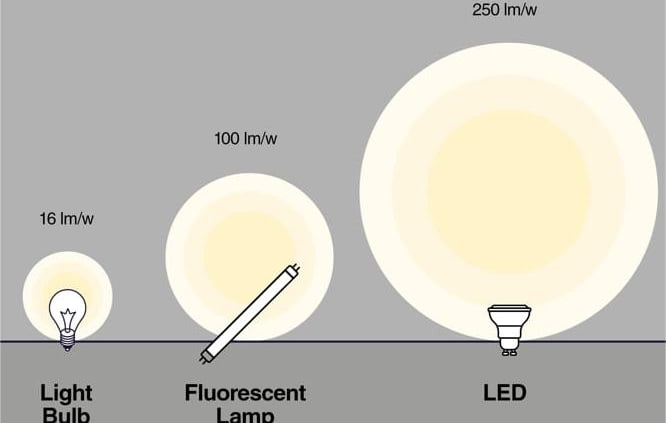
There are two important indicators of the brightness of the farola solar, Lux and Lumens.
Lux and lumens are both units of measurement for brightness. They are used to tell us the amount of illumination output and the brightness of the light falling on a given surface.
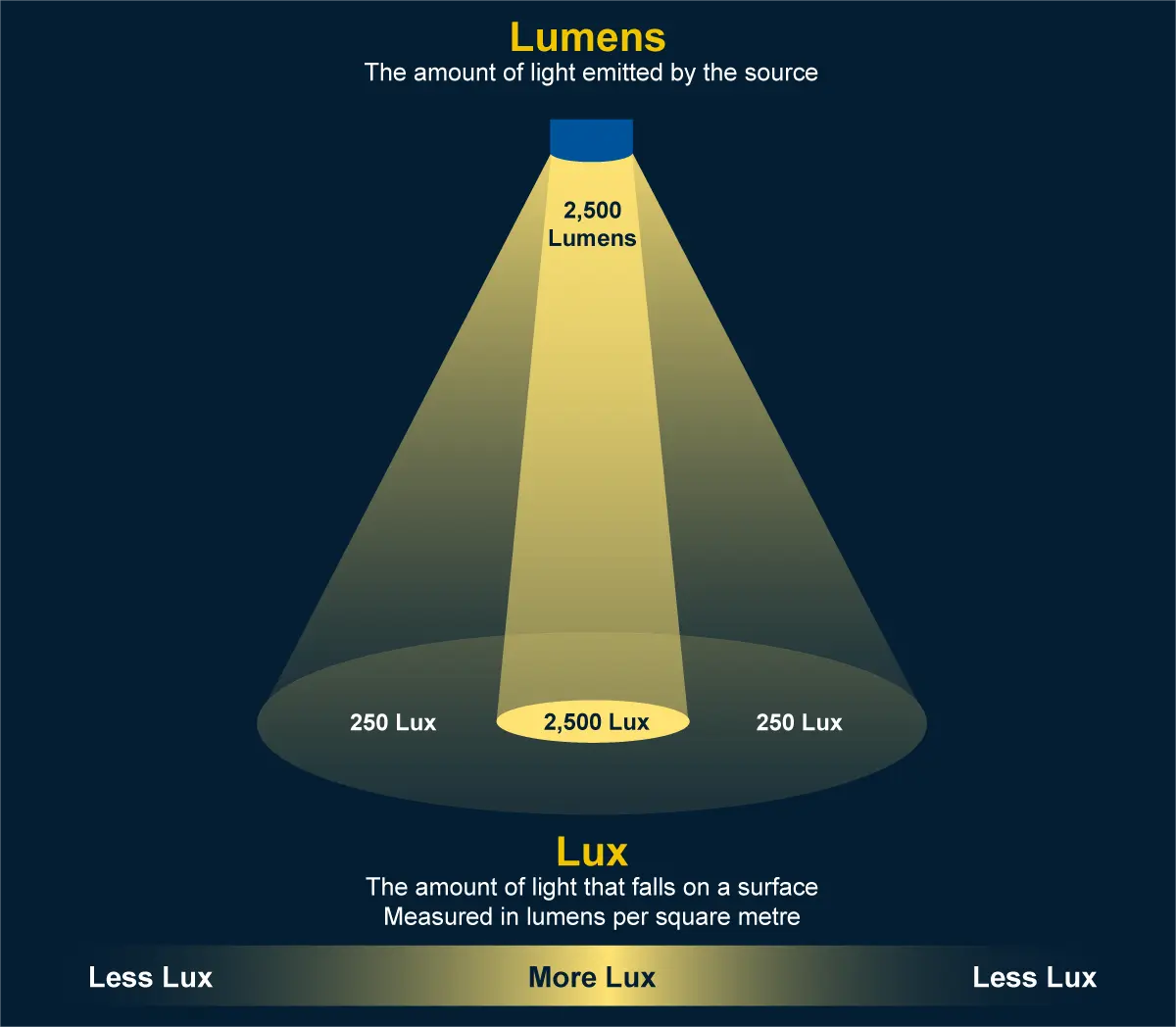
Lumens equals light output.
Lux (represented as lx) stands for luminous flux per unit area.
Relationship between lumens and lux:One lux is equal to one lumen per square meter (lm/m2).
 In this post, we will explore the Lux standards of street lights and why they are important. If you want to learn about lumens you can check out this article:UNDERSTANDING WATTS AND LUMENS: HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT BRIGHTNESS LIGHT FIXTURE FOR YOUR PROJECT
In this post, we will explore the Lux standards of street lights and why they are important. If you want to learn about lumens you can check out this article:UNDERSTANDING WATTS AND LUMENS: HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT BRIGHTNESS LIGHT FIXTURE FOR YOUR PROJECT
¿Qué es Lux y por qué es importante?
Lux is a measurement of the light flux falling on a surface. Lux is the international unit of photometry, a method for measuring light intensity. Lux is used to specify the brightness of light or illumination. It is a standard light measurement for all types of lighting, such as household lights, office lights, car headlights, or street lights.
Por qué el nivel de lux tiene más sentido que el de lumen
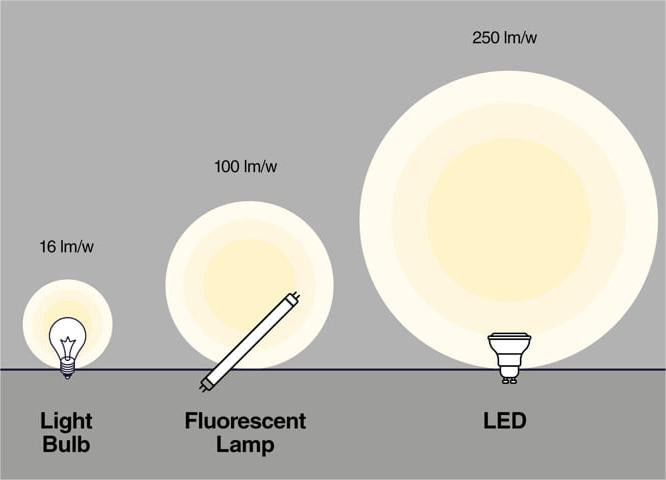
Lumens measure the light output of a single light source. The calculation method for lumens measurement is to multiply the wattage of the light source by the rated lumens per watt of the light source.
Lux is the amount of light on a surface. This can be measured he brightness of light after it travels a certain distance.
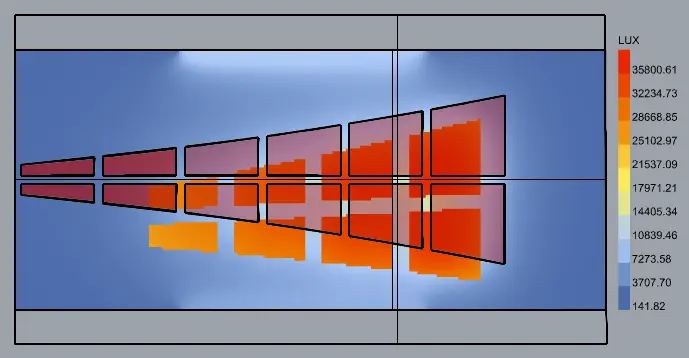
In addition to luminance, Lux levels are the best way to measure the brightness of solar street lights. Illuminance measurement can be easily done with just an illuminance meter, while luminance measurement requires specialized equipment and is more difficult to implement.
Now, when you have a solar street light bulb that produces 1000 lumens, its brightness will be different if placed 10 meters away. Therefore, changing the position of the bulb will change the brightness under different Lux levels. Lumens measure the amount of light produced by the bulb; Lux measures the distance light propagates.
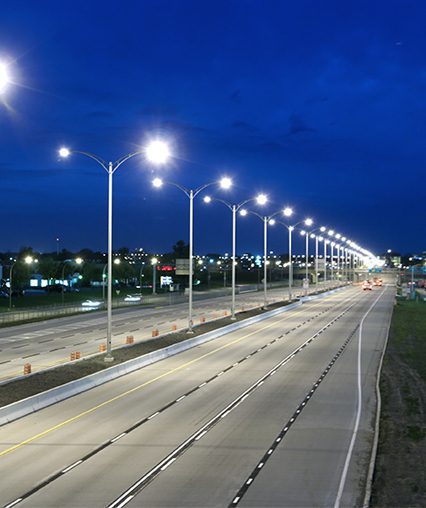
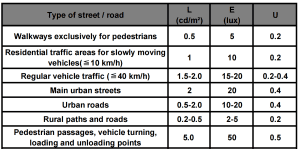
Different road solar street lights Lux levels
According to standards specified in some countries’ government documents, we provide the following recommendations as a reference:
Highway lighting Lux levels

First-class highways, second-class highways: minimum average illuminance maintenance value 20 lx (low standard) / 30 lx (high standard), uniformity minimum value of 0.4;
Third-class highways: minimum average illuminance maintenance value 15 lx (low standard) / 20 lx (high standard), uniformity of 0.4;
Fourth-class roads: average illuminance 10 lx (low standard) / 15 lx (high standard), uniformity of 0.3;
The above illuminance requirements apply only to asphalt roads, and the illuminance requirements for concrete roads can be correspondingly reduced, with a reduction of not more than 30%.
Highway lighting levels should be determined based on the lighting standards of urban roads connected to them, the highway traffic control system, and road partitioning facilities.
The above average illuminance has two standard values, high standard values should be used for the following cases:
- Connected to urban roads with high-grade lighting standards;
- Poor visibility conditions;
- Inadequate highway traffic control systems and road partitioning facilities.
When connected to urban roads with low-grade lighting standards, good visibility, and adequate highway traffic control systems and road partitioning facilities, low-grade values should be used for highway lighting.
Urban road lighting Lux levels

Express roads and main roads: minimum average illuminance maintenance value 20 lx (low standard) / 30 lx (high standard), uniformity minimum value of 0.4;
Secondary roads: minimum average illuminance maintenance value 15 lx (low standard) / 20 lx (high standard), uniformity of 0.4;
Side roads: average illuminance 10 lx (low standard) / 15 lx (high standard), uniformity of 0.3;
The above illuminance requirements apply only to asphalt roads, and the illuminance requirements for concrete roads can be correspondingly reduced, with a reduction of not more than 30%;
City road lighting illuminance values should be determined based on the area where the project is located, road positioning, traffic flow, road partitioning facilities, environmental brightness conditions, and actual needs.
High standard values should be used for the following conditions:
- Central cities and areas, or main roads leading to large public buildings and places in the city;
- Central business districts or main arteries of the city;
- Roads with higher environmental brightness;
- Main roads for people entering and exiting areas such as schools, hospitals, and nursing homes;
- Roads with inadequate road partitioning facilities, mixed traffic of motor vehicles, non-motor vehicles, and pedestrians.
Low standard values are recommended for the following conditions:
- Roads near residential areas and recreational areas;
- Areas with lower environmental brightness.
Rural road lighting Lux levels

Primary roads: minimum average illuminance maintenance value 10 lx (low standard) / 15 lx (high standard), uniformity minimum value of 0.3;
Side streets and lanes: minimum average illuminance maintenance value 5 lx (low standard) / 8 lx (high standard);
Public activity squares: minimum average illuminance maintenance value 10 lx (low standard) / 15 lx (high standard);
The above illuminance requirements apply only to asphalt roads, and the illuminance requirements for concrete roads can be correspondingly reduced, with a reduction of not more than 30%;
Rural road lighting illuminance values should be determined based on the area where the project is located, road positioning, traffic flow, road partitioning facilities, environmental brightness conditions, and actual needs.
High standard values should be used for the following conditions:
- Roads with high traffic flow near towns;
- Large rural roads with dense commercial activities;
- Roads with higher environmental brightness;
- Roads with inadequate road partitioning facilities, mixed traffic of motor vehicles, non-motor vehicles, and pedestrians
Low standard values are recommended for the following conditions:
- Rural roads in remote areas;
- Roads within villages where motor vehicles do not pass through;
- Areas with lower environmental brightness.
Intersection area Lux levels for motor vehicles
- Intersection of Grade 1 with Grade 1, Grade 2, Grade 3: minimum average illuminance maintenance value of 30 lx (low standard) / 50 lx (high standard), uniformity maintenance value of 0.4;
- Intersection of Grade 2 with Grade 2, Grade 3: minimum average illuminance maintenance value of 20 lx (low standard) / 30 lx (high standard), uniformity of 0.4;
- Intersection of Grade 3 with Grade 3: minimum average illuminance maintenance value of 15 lx (low standard) / 20 lx (high standard), uniformity of 0.4;
When the lighting standards at the intersecting roads are both low standard illuminance values, the intersection area should adopt the low standard value, otherwise, the high standard value should be used.
Pedestrian overpass lighting Lux standards
- For pedestrian overpasses with high human flow in rural areas and low human flow in cities: average illuminance of 5lx on the bridge deck, average illuminance of >6lx on the stairway path;
- For pedestrian overpasses with high human flow in cities: average illuminance of 10lx on the bridge deck, average illuminance of >12lx on the stairway path;
- For semi-enclosed pedestrian overpasses: average illuminance of 30lx on the bridge deck, average illuminance of >36lx on the stairway path;